When considering life on Earth, humans, plants, exotic animals, and landscapes, such as the alien life NASA claims to be investigating at Yellowstone National Park.
However, there is a tendency to overlook the many species of microscopic organisms, which, actually, outnumber all the bugs, mammals, birds, and plants on planet Earth combined. These microscopic organisms exist in nearly every environment on Earth, regardless of how extreme the climate, from deep-sea thermal vents to the highest peaks of the Himalayas.
These microscopic organisms vary significantly, with some microorganisms like water bears resembling four-legged creatures, others resembling long, wiggling worms, and still more not resembling anything known to man.
The Earth’s oceans in particular contain a wide variety of microorganisms, some with the ability to glow in the dark in a phenomenon known as bioluminescence, allowing large clusters of them to be seen from outer space. And just recently, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) detected a giant glowing “creature” off the coast of Australia that has already amazed scientists and curious nature lovers all over the world.
NASA Spots This Natural Wonder From Space
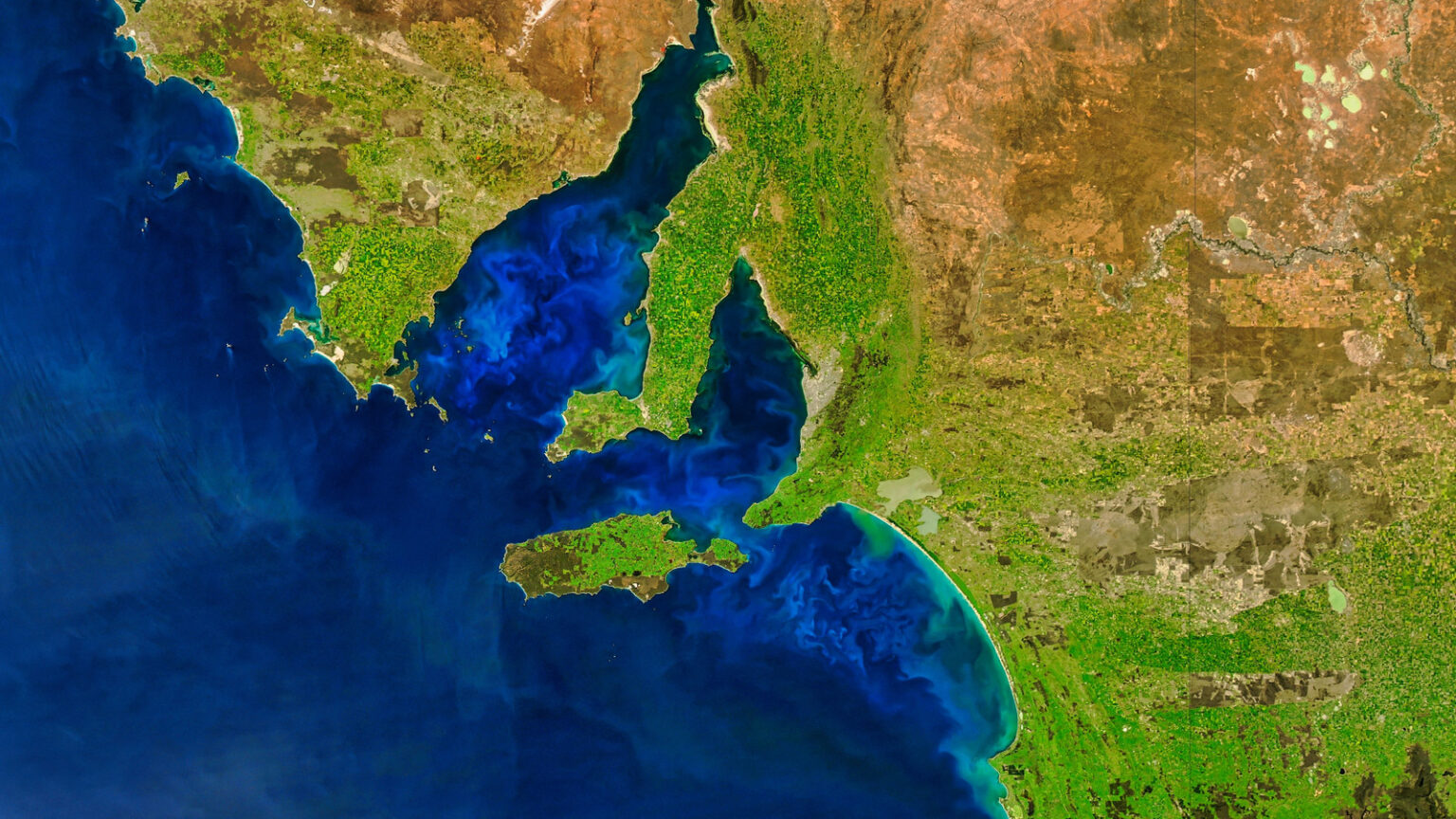
Recently, NASA spotted a large patch of a curious, glowing material located off Australia’s southern coast, between the mainland and the island of Tasmania, in an area known as the Bonney Coast. Scientists quickly identified this glowing patch as a massive cluster of bioluminescent phytoplankton, which are found in oceans worldwide. However, this massive patch of phytoplankton was abnormally large and bright, allowing NASA scientists to spot it from outer space with ease.
NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft first spotted this mesmerizing natural phenomenon by using its highly sophisticated Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), which allowed the spacecraft to spot the massive cluster of phytoplankton from space.
NASA launched PACE in 2024, and so far, PACE has served as a vitally important tool for scientists as they try to learn more about phytoplankton in every corner of the globe and the crucial role it plays in various ecosystems. The data and information provided by PACE have already proved crucial in the global fight to protect the environment, which includes protecting small microorganisms, which ultimately fuel the food chain, which goes all the way up to human beings.
Why Bioluminescent Phytoplankton Tend To Glow In Southern Australia
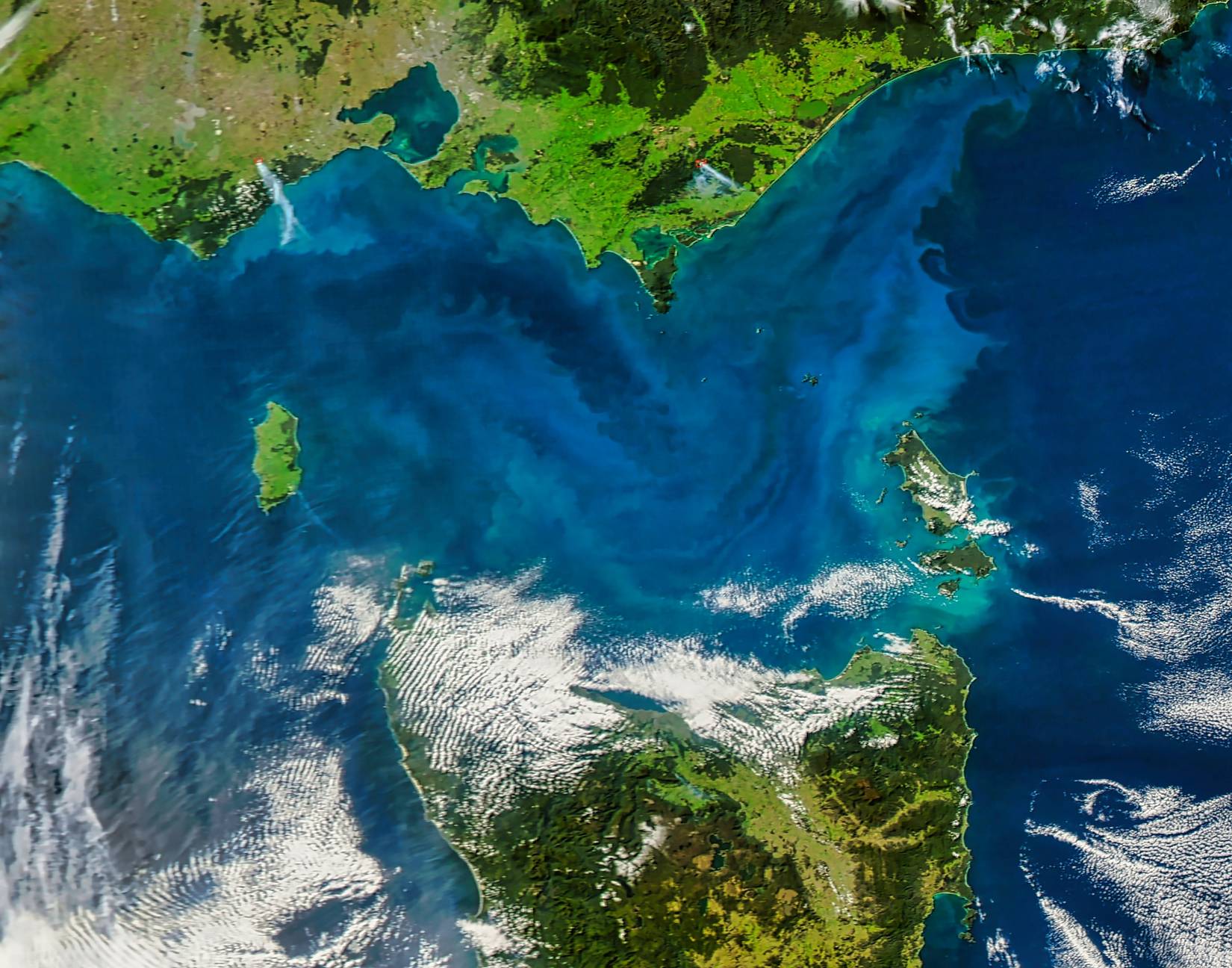

Phytoplankton bloom in Bass Strait, Australia with elements of this image furnished by NASACredit: Shutterstock
Scientists have identified the Bass Strait, or the body of water that separates the southern coast of Australia and the popular tourist destination and island of Tasmania, and the waters off the Bonney Coast, as a popular spot for dinoflagellates to collect and glow spectacularly.
The Bass Strait and its surrounding coasts serve as a vitally important channel for marine life, meaning that numerous marine animals of all shapes and sizes die in this area regularly. The nitrogen and phosphorus that these decaying creatures leave behind serve as the primary fuel for dinoflagellates, meaning that they thrive in places such as the Bass Strait and the areas near this crucially important strait.
Best Places to Experience Beautiful Bioluminescent Phytoplankton
According to National Geographic, these are the best locations worldwide to witness the bioluminescent phytoplankton phenomenon-
Location
Area
Best Time
Puerto Rico, Caribbean
Mosquito Bay, Fajardo’s Laguna Grande
year-round
New South Wales, Australia
Barfleur Beach or Blenheim Beach in Jervis Bay
Between May & August
Krabi, Thailand
Railay Beach
Between November & May
Matsu Islands, Taiwan
Matsu Islands (Beigan & Qiaozi Village)
April to June
Oaxaca, Mexico
Escondido’s Laguna Manialtepec
June & July
California, USA
San Diego’s Mission Bay & Newport Beach
October & November
Wales, U.K.
Dunvegan Bay & Anglesey’s Penmon Point
Mid to late June
Other locations across the globe that host these massive collections of beautiful bioluminescent phytoplankton include places along the east coast where the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean lies, the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of California, and other places on Earth abundant with marine life.
Without the presence of this bioluminescent phytoplankton, life could not flourish, given the crucial role these tiny organisms play in the ecosystems of these places. A wide array of sea life directly feeds off of this phytoplankton, with many species of fish feeding on those creatures, with humans in turn feeding on those fish.
How The Smallest Of Organisms Create Amazing Spectacles
Scientists refer to the bioluminescent phytoplankton, such as those recently spotted off the Bonney coast of Australia, as dinoflagellates, which combine the Greek word for “whirling,” “Dinos”, and the Latin word “flagellum,” which means “whips.” These dinoflagellates, which often measure anywhere from 30 micrometers to several millimeters in width, serve as the foundation of many food chains worldwide, feeding the creatures that fish feed on, which people in turn rely on for food.
Given the immense importance of these microorganisms, scientists all over the world have invested massive sums in studying these tiny creatures, which play an important role in the global ecosystem. NASA’s PACE spacecraft represents one of the most significant investments in studying these microorganisms, and already, this spacecraft has changed how many people view them. Many of these organisms have developed bioluminescence as a defense mechanism, designed to scare off certain predators, while also attracting larger creatures with the hope that they will consume the smaller predators.
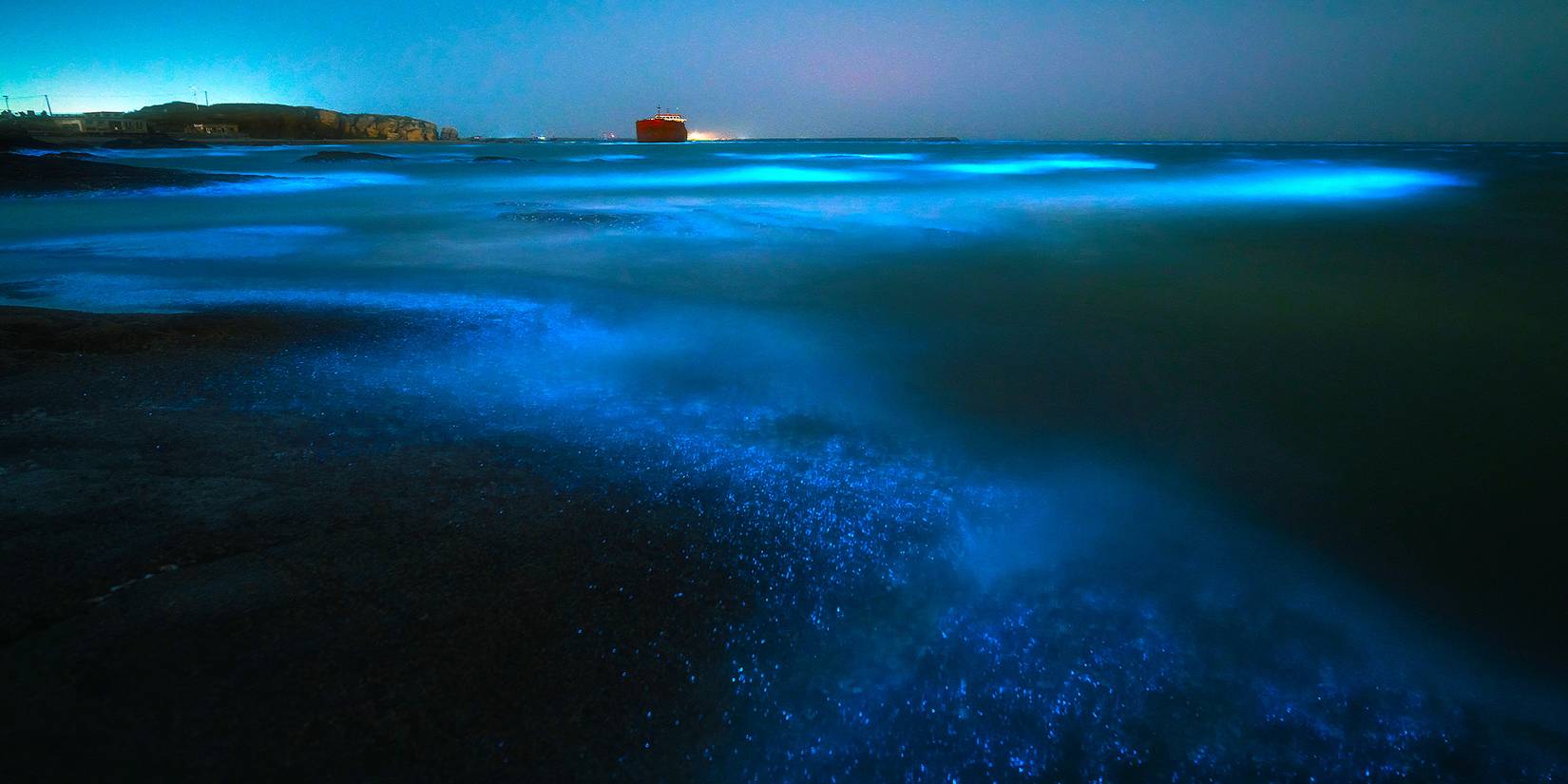

Nighttime image of a beach with a red boat on the horizon and bioluminescent algae in the waterCredit: Shutterstock
The bioluminescent dinoflagellates only glow at night, thanks to their circadian clock, which is similar to the one humans have, helping them determine when to wake up and go to sleep. Scientists have conducted several studies regarding circadian clocks, including a scientist who plunged himself into a cave for months to understand this phenomenon better. Beachgoers can often see these microorganisms glow at night when they splash in the water, which appears as blue and green sparkles.

Space view on Planet Earth and Sun Star rotating on its axis in black Universe. Seamless loop with day and night city lights change. Astronomy and science concept.Credit: Shutterstock
The images recently taken of massive phytoplankton growth off the coast of Southern Australia remind people across the globe of the vast array of living creatures that call planet Earth home. Although scientists can only observe these creatures with a powerful microscope, they play an immensely important role in the global ecosystem, serving as food for many species of marine life while also helping to balance the presence of gases such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
NASA’s PACE probe helps to keep a watchful eye on crucial species of microorganisms from outer space, allowing scientists to take decisive steps towards protecting the environment.