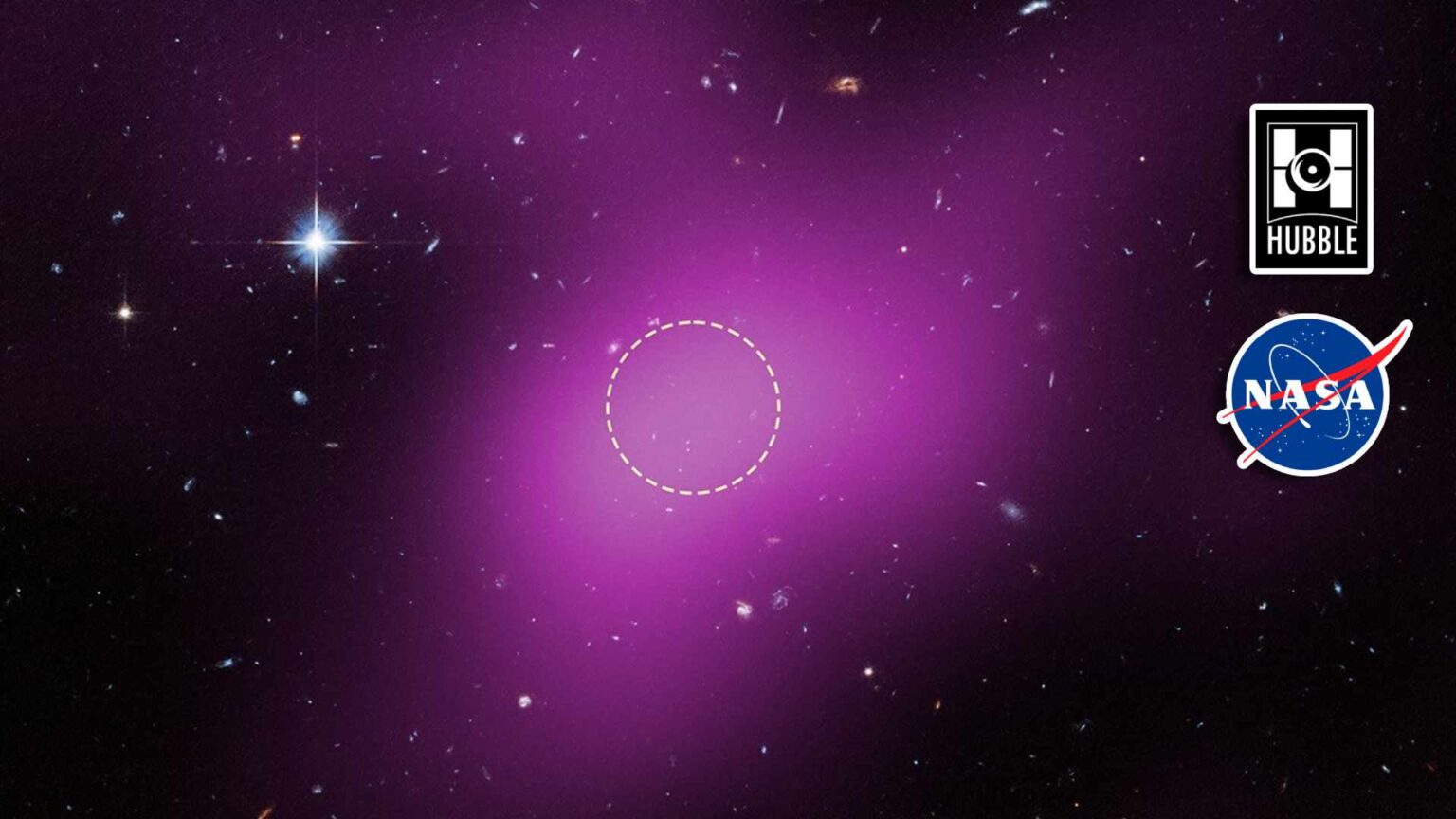
Cloud-9
Composition and Size: The object features a core of neutral hydrogen spanning approximately 4,900 light-years in diameter.
Gas Mass: Based on radio wave emissions, researchers estimated the hydrogen gas mass to be roughly one million times that of the Sun.
Dark Matter Mass: Calculations indicate the object contains approximately five billion solar masses’ worth of dark matter.
Structural Balance: The dark matter’s gravitational pull appears to be balanced by internal gas pressure.
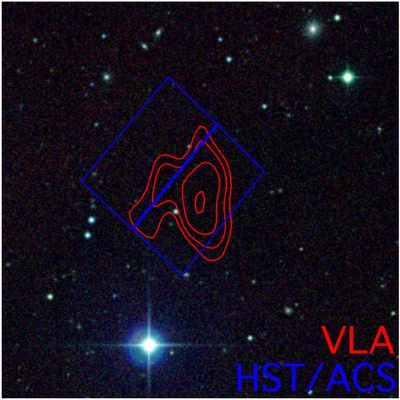
Image: Gagandeep Etal | AAS Journals
Researchers have stumbled upon a new form of astronomical object, hitherto unseen (or unnoticed), using NASA’s Hubble telescope. “A starless, gas-rich, dark-matter cloud, nicknamed Cloud-9.”
What a way to commence 2026 with a bizarre new discovery! The object nicknamed Cloud-9 is scientifically known as Reionization-Limited H I Cloud or “RELHIC,” where “HI” refers to neutral hydrogen. Per NASA “RELHIC” describes a natal hydrogen cloud from the universe’s early days, a fossil leftover that has not formed stars.”
Principal investigator Alejandro Benitez-Llambay of the Milano-Bicocca University in Milan, Italy stated in the study that,
“This is a tale of a failed galaxy.”
He added, “In science, we usually learn more from the failures than from the successes. In this case, seeing no stars is what proves the theory right. It tells us that we have found in the local universe a primordial building block of a galaxy that hasn’t formed.”
Andrew Fox of the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy/Space Telescope Science Institute (AURA/STScI) for the European Space Agency, a member of the project, noted,
“This cloud is a window into the dark universe.”
He added, “We know from theory that most of the mass in the universe is expected to be dark matter, but it’s difficult to detect this dark material because it doesn’t emit light. Cloud-9 gives us a rare look at a dark-matter-dominated cloud.”
Lead author Gagandeep Anand of STScI remarked, “Before we used Hubble, you could argue that this is a faint dwarf galaxy that we could not see with ground-based telescopes. They just didn’t go deep enough in sensitivity to uncover stars.” He further added, “But with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys, we’re able to nail down that there’s nothing there.”
A team using @NASAHubble has made the first confirmed detection of a new type of astronomical object: a starless, gas-rich, dark-matter cloud, nicknamed Cloud-9. Here’s what this object is teaching us about dark matter and the early universe: https://t.co/csCRXnzgDM pic.twitter.com/ZnUnhy9EYL
— NASA (@NASA) January 5, 2026
🆕 New astronomical object just dropped!
This starless, dark-matter-dominated cloud, nicknamed ‘Cloud-9’, is the first such object seen in the Universe. 1/3 pic.twitter.com/BV0gr1H0Ae
— HUBBLE (@HUBBLE_space) January 5, 2026
This is a “failed galaxy”: a starless, gas-rich, dark-matter cloud considered a remnant of early galaxy formation.
Nicknamed “Cloud-9,” this is the first confirmed detection of such an object in the universe: https://t.co/QXAbbc4FgX#AAS247 pic.twitter.com/od8COZqXaq
— Hubble (@NASAHubble) January 5, 2026
Scientists trained Hubble’s sharp vision on a starless, gas-rich, dark-matter cloud and identified a new type of astronomical object—a failed galaxy that never produced stars. Nicknamed Cloud-9, it is considered a fossil from the early universe: https://t.co/nxdwdPsSQI #AAS247 pic.twitter.com/BrMt4mBPbn
— Space Telescope Science Institute (@SpaceTelescope) January 5, 2026
More info on Cloud-9 here.
See Also: Universe Is 26 Billion Years Old, Dark Matter Doesn’t Exist: Indian-Origin Scientist In New Study
See Also: Stars In The Universe Might Have Been Driven By Annihilating Dark Matter
See Also: From Kissing Number Problem To The Big Void, 10 Scientific Mysteries That Remains Unsolved In 2025
Cover: NASA