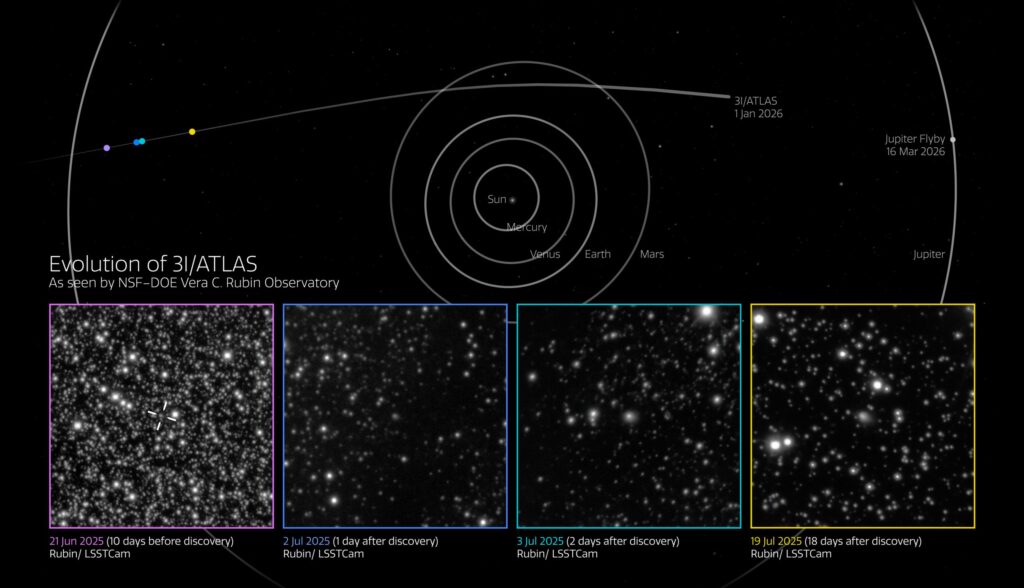
The NOIRLab research center has published images taken by the Vera Rubin Observatory. They show the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS. The photos were taken 10 days before its official discovery.
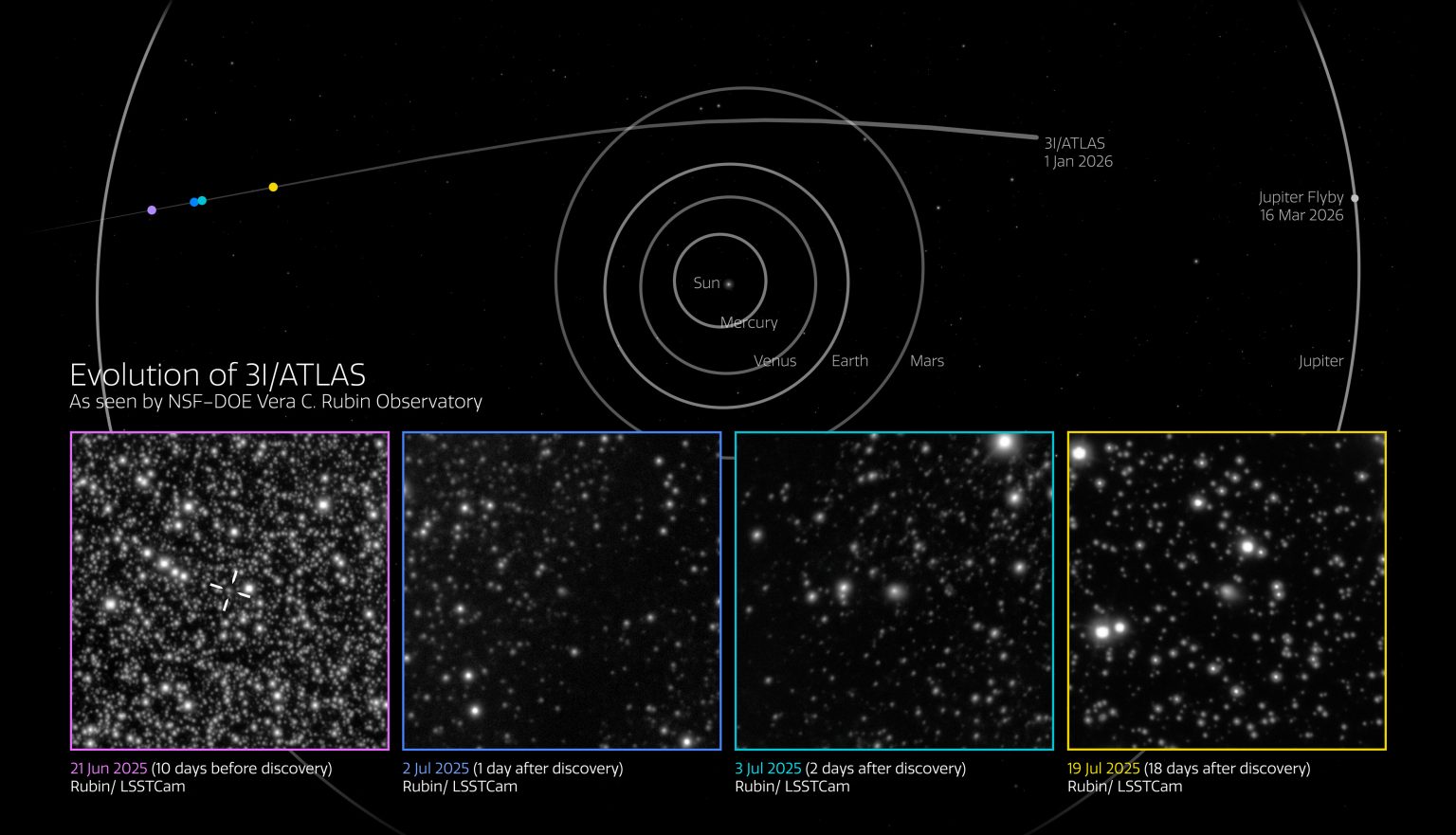 Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS in images taken by the Vera Rubin Observatory between June 21 and July 19, 2025. Source: NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory/NOIRLab/SLAC/AURA
Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS in images taken by the Vera Rubin Observatory between June 21 and July 19, 2025. Source: NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory/NOIRLab/SLAC/AURA
The Vera Rubin Observatory is located in Chile. It is an 8.4-meter wide-angle survey telescope with the largest field of view of any existing astronomical instrument. It is designed to capture images of large areas of the sky at once.
The Vera Rubin Observatory officially saw the light of day on June 23, 2025, when its first official images were published. However, it had been conducting test observations even before that. And, as it turned out, during those observations, it managed to capture a very interesting object — the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS.
The interstellar comet was discovered on July 1, 2025, by telescopes belonging to the automated ATLAS system. Upon learning of this, staff at the Vera Rubin Observatory reviewed images taken during testing. The review showed that, thanks to its unprecedented field of view and light-gathering ability, as well as a necessary dose of luck, it photographed the comet ten days before its formal discovery.
The observatory continued to observe 3I/ATLAS until July 20, 2025. The LSST camera took nearly 100 exposures, which show a time-lapse of the interstellar object moving across the night sky. It managed to capture the small details of the comet’s evolution as it approached the Sun.
According to scientists, a huge number of interstellar objects regularly pass through the Solar System. But they are extremely difficult to detect, as they are only visible when they are bright enough or close enough, and our telescopes are pointed in the right place at the right time. For this reason, the astronomical community eagerly awaited the start of operations at the Vera Rubin Observatory. It will be able to find millions of changes in the sky and discover an unpredictable number of previously unknown interstellar objects.A
ccording to NOIRLab